






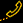
Database Access Method
Accessing the database form applications, many solutions are provided. The main type of architecture solutions for database access are shown as following:
1. Manually written program using native-database API or database-independent API libraries
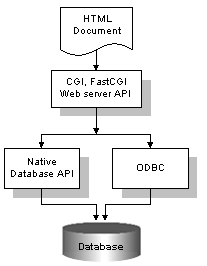
Database API libraries are collection of functions or object classes that will provide source code an access to the databases. Developers can write program mainly in CGI, FastCGI, server API using database API libraries to make an application able of accessing data stored in database (see Figure 3.3).
This method is the foundation of every database-based application on Internet. Other methods also use database APIs and the supporting gateways (CGI, server API, etc) but they add additional layer of programming to provide the developer a different, easier, or more customized programming interface.
Most or all of the database vendors provide their native-database API libraries. Using these API libraries, developers have to add code that talks to a particular database using a proprietary language. If the program needs to access to different types of databases, for example, Access, Foxpro and Oracle databases, it have to be coded with three different database languages. When programming to interact with ODBC the programmer needs to code program with the ODBC language (a combination of ODBC API function calls and the SQL language). Regardless of the database type developers are using, all of their calls will be to the ODBC API. All that one needs to do is have installed an ODBC driver that is specific to the type of database one will be using.
There are many database API libraries provided by vendors as shown in the following table:
Database API libraries/class libraries products
|
Database Vendor |
API /Class libraries |
|
Oracle |
Pro*C, OraPerl, DBI w/DBD::Oracle |
|
Informix |
ESQL, DBI w/DBD::Informix |
|
Sybase |
SybPerl, DBI w/DBD::Sybase |
|
MSQL |
MsqlPerl |

Architecture of application using direct access to database by native-database API or database-independent: ODBC
Advantages
Disadvantages
2. SQL-embedded Template-driven database access packages
These packages usually consist of:
Creating application by such a package is easy. The developers just create a template using standard HTML and special tags. This solution is suitable for the application that does not require complex manipulation and need speed of development.
Advantages
Disadvantages
There are many SQL-embedded Template-driven packages provided by vendors as shown in the following table:
SQL-embedded template-driven packages provided in different vendors
|
Database Vendor |
Template package |
|
IBM |
Net.data |
|
Informix |
Web DataBlade |
|
Sybase |
Web.sql |
|
MSQL |
W3-mSQL |
To select the package for developing the application, developers should consider the following criteria;
3. Java/JDBC
This solution benefits from Java programming language, which make an application to be platform-independent. Java applets or Java applications will be downloaded and run on client machines having the Java virtual machine (VM). As a result, workload on the server-side can be reduced.
JDBC is a SQL database access interface. JDBC API gives Java developers a common API to most relational databases. It is expressed through several abstract Java interfaces. The JDBC API standard defines a set of Java classes required to perform standard relational database operations such as managing database connections, SQL statements, result sets, and metadata. Like ODBC, the JDBC API uses a driver manager that simultaneously supports multiple database drivers for various databases. The driver(s) can be downloaded with the applet or exist as native drivers on the client.
Java developers also have the option of interfacing directly with ODBC through a JDBC-ODBC bridge.
Applications in this solution can be created in two models: two-tier model and three-tier model
Two-tier model
In this model, A Java applet connects directly to the database. The applet is downloaded from Web server and executed within the Java-enabled browser environment. The applet uses JDBC to connect back to a database server (see Figure 3.4). This model requires a JDBC driver that can communicate with the particular database on the client machine.

Two-tier model of JAVA/JDBC applications
Three-tier model
With the three-tier architecture, the Java applet or application makes a call to a service layer at the middle tier. This layer can be a transaction-processing monitor, object request broker (ORB), Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI), or Web server API (CGI, ISAPI, or NSAPI). The middle-tier service, in turn, makes a call to a database server. The database processes the request and sends the results back to the middle tier, which then sends them to the browser.
In many cases, this model provide advantages because the middle tier makes it possible to maintain control over access to corporate data and when there is a middle-tier the user can employ a higher-lever API which is translated by the middle tier into the appropriate low-level calls.
Three-tier model of JAVA/JDBC applications
Advantages of Java/JDBC
Disadvantages of Java/JDBC
4. Database Vendor Solution
Today, each of the major database vendors has a new suite of internet-access product available to bridge their database with the web applications. For example Oracle�s Oracle Lite 3.5 were added Java-related features including JDBC support, the ability to create triggers and stored procedures in Java, the ability to use Java access classes to store Java objects, and the management of data through a Java-enabled browser application.
Sybase�s Adaptive Server Anywhere 6.0 provides a Java run time environment in the database server. It allows developers to store Java objects in database tables by using a Java class as a data type for a column in a table. Adaptive Server Anywhere also supports JDBC as an interface from client applications using the Sybase jConnect JDBC driver.
Microsoft�s IDC/HTX, IDC (Internet Database Connector) is a component of the Microsoft Internet Information Server. IDC accepts input form a Browser to execute SQL commands against an ODBC data source and return any resulting data to browser formatted as defined in HTML template (htx). This solution is suitable for the organizations that are using windows NT and ODBC-compliant database.
These solutions might be a choice of the corporations who have an existing database and have already spent a lot of money with the database engines and supporting products. It might be more economical to choose such a solution.
5. Other Web Database tools
There are a number of web database products available in the market to simplify the development, by hiding the database connectivity details from the developers. Some tools such as Web database visual building tools provide user-friendly interface. Some tools can generate applications in a different language, for example Sapphire/Web generates CGI program by C or C++ code and that CGI program connects to any database designed by the user and sends queries for processing. Net.Dynamics works similarly. It generates application in Java code.
The architecture and technologies used by these tools are different, so each one must be considered on its own. To select a product depends mainly on the databases that the tool can be able to access. But the developer should know the following detail of the tools so that the decision can be made correctly.
Advantages
Disadvantages
| Previous | Contents |
 |
| Designed by Chollada Wiyaporn. |
| Copyright � 1998. All Rights Reserved |